2376-0249
Case Blog - International Journal of Clinical & Medical Images (2019) Volume 6, Issue 2
Author(s): AS Prasanth, G Mahilrajan, S Pirasath
Case History
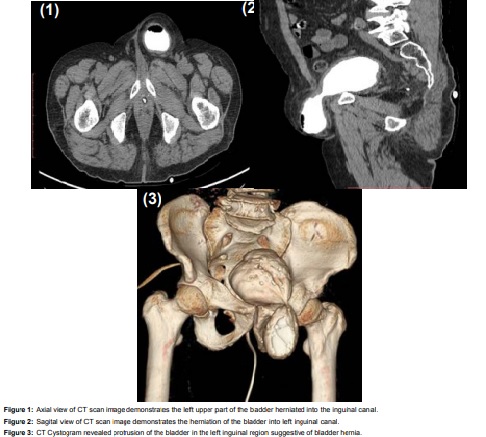
Herniation of the urinary bladder into the inguinal canal is rare and constitutes 1–3% of all inguinal hernias. Bladder herniation is usually asymptomatic and is determined incidentally; however, it may rarely present with urinary obstruction symptoms. Here, we described an incidental bladder hernia in a 76-year-old man who is evaluated in radiology department for fever and left-sided flank pain for three days duration. He had no previous history of trauma, medication abuse, surgery or familial bladder disorders. His additional co morbidities included hypertension and diabetes mellitus. There were no remarkable findings on abdominal examination except left side loin tenderness. On evaluation Computed tomography (CT) revealed that a left inguinal hernia with fluid density lesion continuous with left lateral bladder wall. No bowel was contained in the hernia (Figure 1, 2). The inguinal hernia was confirmed as bladder hernia by CT cystogram (Figure 3). Inguinal hernia usually contains the peritoneum that surrounds the abdominal organs. Bowel loops, omentum, or extraperitoneal fat can be detected within the hernia sac in the inguinal canal. However, as in this case, the bladder can also be present within the hernia sac. Early diagnosis with radiological imaging is important to prevent complications during surgery.
 Awards Nomination
Awards Nomination

